Reproduction in Humans
Male reproductive system
1.Sperms have a tail whereas eggs do not. Why so? (C.B.S.E. 2007)
2.Why does failure of testes to descend into scrotum produce sterility?
3.Mention the difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation.(C.B.S.E. 2012)
4.Where is acrosome present in humans? Write its functions. (C.B.S.E. 2012)
5.Mention the location and function of Leydig cells in humans. (C.B.S.E. 2012)
6.Mention the function of mitochondria in sperm. (C.B.S.E. 2012)
(a) Give a schematic representation of spermatogenesis in humans.
(b) At which stage of life does gametogenesis begin in human male?
(c)Describe the structure of a human sperm.
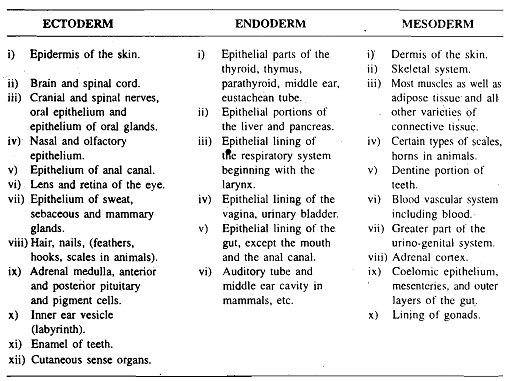
Fate of Germ Layers
List the following events observed in human reproduction in chronological order.
Fertilization, gametogenesis, insemination, gestation, parturition, implantation.
State the significance of cervix in the female reproductive system.
What is the reason for the absence of menstrual cycles during conception or pregnancy?
Fill up the missing data in the table where Column A shows female reproductive organs and Column B shows its respective functions.
| Column A (Organs) | Column B (Corresponding Functions) |
| Ovaries | Ovulation |
| Oviduct | |
| Pregnancy | |
| Vagina | Birth |
State the role of the epididymis in male fertility.
List the names of the hormones, endocrine glands along with functions of the hormones that are crucial in causing spermatogenesis.
Fill in the missing boxes for the levels in the transformation of mother germ cells into a mature follicle.


What are the events that cause the chromosome number of gametes to go from 2n, n, and again back to 2n during reproduction?
How is a primary oocyte different from a secondary oocyte?
State the role of the ampullary-isthmic junction in the female reproductive tract.
How is polyspermy checked by the zona pellucida of the ovum?
What is the significance of LH surge through the menstrual cycle?
State the significance of the following stages during the lifetime of a female.
- Menarche
- Menopause
Why does corpus luteum stay active throughout pregnancy and in the absence of fertilization, is active only for 10-12 days?


Comments
Post a Comment